Jewelry Quality

Design
The first person to “see” the designer’s idea is a blank sheet on which the idea takes on graphic contours. For a detailed study and creation of a technical drawing, important for the subsequent stages of production, the sketch is transferred to a computer and, using a tablet and a pen, is brought to perfection.
3D modeling
The technical drawing created by the artists falls into the hands of 3D designers, who show considerable creativity by creating a three-dimensional model of the decoration in a professional computer program. Computer modelers work closely with the artists to fully convey their intent.
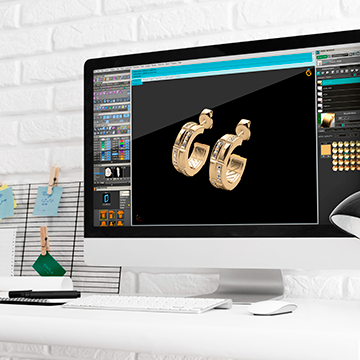

Prototyping
A computer file with a model of a piece of jewelry developed by 3D designers is transferred to prototyping. The future piece of jewelry is “grown” on a special 3D printer made of polymer or wax. The model created on the equipment is finalized by the fashion designer for subsequent casting.
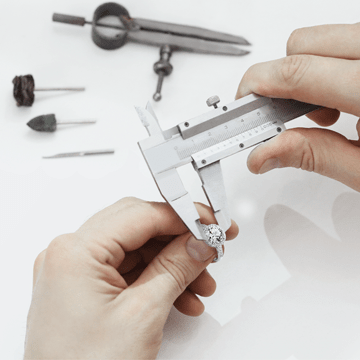
Modeling
Regardless of what metal the jewelry was conceived from, it first appears in silver. Many prototypes are put on wax rods and cast in metal. After the final refinement by the fashion designer, they become a master model – a prototype of the future circulation of jewelry.
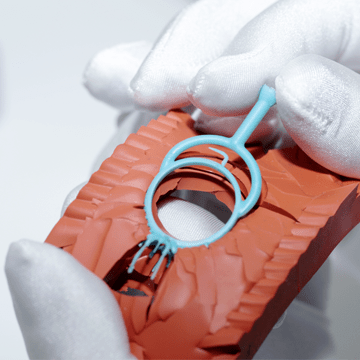
Mold making
The master model is used by jewelers to obtain a mold. The prototype is immersed in a special plastic mass, molded and sent to an oven, where at a high temperature the plasticine-like mass hardens to the state of rubber. The mold is carefully cut and the master model is removed.
Wax modeling
The modeler of lost-wax models tightly clamps the mold, into which molten wax is poured under pressure, takes the shape of the future product and instantly hardens. Prototypes of jewelry are put on a wax rod, getting a blank for casting, similar to a Christmas tree.


Casting
The wax yolk is placed in a special form – a flask, which includes the molding mass and the need for it. The plaster hardens and the wax models melt. The flask is removed, it is allowed to cool, then it is loaded with jewelry alloy. After casting, the solid mold mass is washed off, and the Christmas tree in the metal is lit. Products are cut off and sent for exceptional processing.
Grinding
Freshly cast products are matte and devoid of shine. Grinding gives the metal a certain purity and surface dimensions. With the help of a grinding machine, the master “collects” excess metal. To process the smallest details, a hand tool is used – a drill for processing nozzles or a file.


Tumbling and Polishing
Products are placed in rotating drums with special polishing agents or reagents. Usually tumbling includes two stages: wet grinding and dry polishing. Specialists load and unload products, keep track of time: it is important to correctly set the parameters of the equipment and not damage the metal.
Mount
Complex pieces of jewelry are sent to the mount site. Here they connect the decorative part and the lock at the earrings, attach rings to the pendants, assemble complex bracelets and perform many other operations. The strength of the assembly is checked by quality control.


Stone setting
One of the laborious and responsible stages of production. Experienced specialists work with a microscope, carefully placing inserts – from cubic zirkonia to diamonds – into special platforms and fixing them. At this stage, professionals with many years of experience work, and all stones are attached exclusively by hand.
Galvanization
Jewelry made of white metal is covered with noble rhodium – a metal of the platinum group. Products are lowered into a galvanic bath, where, as a result of a chemical reaction, they are covered with an even layer of metal. On products made of red gold, rhodium is applied with a special pencil, as a rule, in the places where the inserts are attached.


Final check
At the final stage, the jewelry is carefully checked by the quality control service. Only products that meet strict standards receive the ESNOLA tag, which is a certificate of decoration. After that, the jewelry is sent to partner jewelry stores.


